Are you amazed by the technological advancements of the world lately…?
For instance, the advent of self-driving cars like the Autopilot by Tesla, the Audi pilot driving system, speech to recognition, pixel recursive super resolution of video games, recommender system application from e-commerce like Amazon suggesting suitable products, to social media platforms like Instagram or Pinterest and also entertainment such as Netflix movies, Spotify musics, Youtube and the likes…
If yes, then I feel you might be curious to know the workings behind these stunning achievements. The success of these advancements can be ascribed to the concepts like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning, thus stay tuned as I skim through the schema of these concepts.
To start with, the field of Artificial Intelligence (A.I) was formally founded in 1956, at a conference at Dartmouth College, in Hanover, New Hampshire where the term ‘’Artificial Intelligence’’ was coined. A.I is the science of getting machines to mimic the behavior of humans or any living entity. However, Machine Learning (ML) is an application of A.I where a computer learns from past experiences (inputs data) and adapts to become more accurate at making future predictions without following explicit instructions. The performance of such a system should be atleast at human level.
How does the machine learn and carry out predictions…?
In order to perform any task, ML provides various techniques that can learn from and make predictions on a dataset. Most of them follow the same general structure as seen in Figure 1 below.
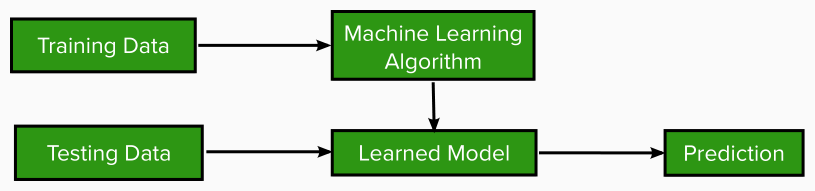
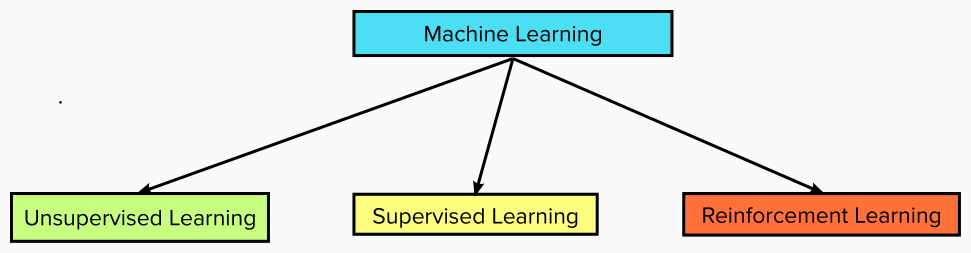
The ML process starts with inputting training data into the selected algorithm, the system analyzes the pattern in the data, by understanding the relationship between the features and the targets, thus develops a learned model based on this. Afterwards, another dataset (testing data) is fed into the learned model to evaluate its performance. This process might be repeated multiple times until a desired level of performance is achieved, then the model can be used to make predictions on unseen datasets. There are several algorithms that can be used for the data modeling which depends on the use case, most of which are categorized as in Figure 2 below.
Unsupervised Learning
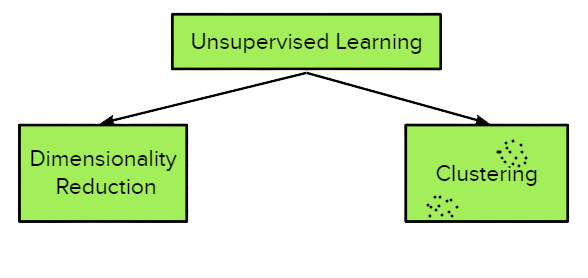
The concept of recommender systems earlier talked about is actually one of many applications of unsupervised learning. An unsupervised learning is a type of ML in which the models are trained using an unlabelled dataset and are allowed to act on that data without any supervision. The task here is to discover interesting attributes about the data without knowing the true answer. And it is divided into two parts as seen in Figure 3 below.
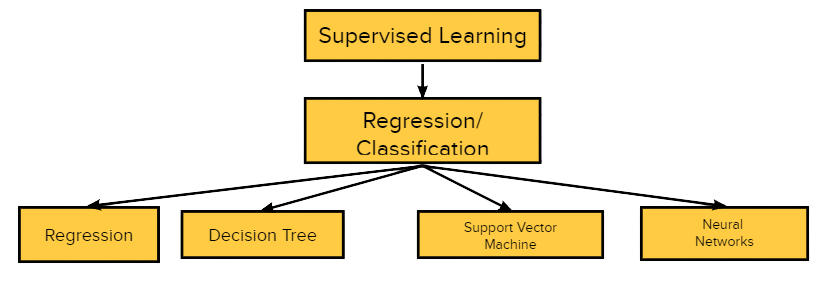
Supervised learning:
Conversely, Supervised learning is defined by its use of labeled datasets to train algorithms that are used to classify data or predict outcomes of an instance with a level of accuracy. The Figure 4 below explains its divisions.
Furthermore, building realistic and natural driving behavior, predicting what other cars might do in the next second, making decisions and few other features of self-driving cars we discussed earlier are puzzle pieces of deep learning which leverage the concept of supervised learning.
What is Deep Learning….?
Deep Learning is simply the name used for stacked Neural Networks, that is, Neural Networks composed of several layers. Neural Networks are input and output systems with a layer structure. The machine learning process is inspired by the functioning of neurons in the human brain. Basically, it comprises of three major components that is; the input layer which propagates the input signal (features), the hidden layer which is made up of the computational units neuron (elaborating the signal from the previous layer) and lastly, the output layer that provides the final output signal all linked by weighted connection as seen in Figure 5 below.
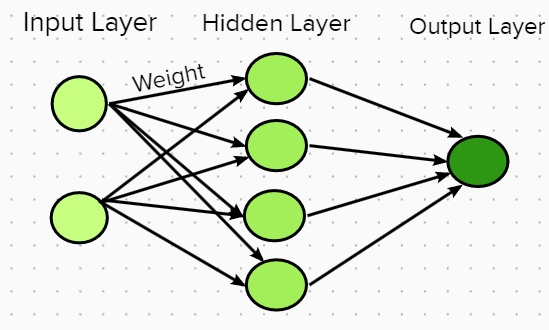
Just like other ML models, the training, the evaluation and the optimization of the model to achieve a desired performance is the path to building any model. Obviously, this is just like an excerpt of fields involved in the success of the aforementioned advancements.
Lastly, the robustness of each field can not be overemphasized, for instance, the concept of neural networks have demonstrated outstanding performance in several research fields to provide solutions to problems that seem complicated and which prompted the idea to leverage the concept to predict results of mechanical models in our ongoing project. In this project, we aim at investigating the ability of neural networks to approximate the results of mechanical models and their performance in terms of precision given some thresholds. The features of the dataset being used include parameters of the geometry, material properties, and applied forces while the target output is resistance or reserved factors. It is part of our objectives to explore different configurations of neural networks models and conduct hyperparameter tuning using different techniques to achieve the expected results.
For now, permit me to stop right here. I will keep you posted with the progress of the work, please stay tuned and feel free to share your comment in the section below…

Leave a Reply