Scheduling on Novel and Advanced Hardware
Project reference: 1812
The aim of this project is to explore the effects of upcoming novel hardware, such as NVRAM, on HPC job scheduling. By adapting a workload simulator that is being developed at EPCC to model new hardware, and by using traces of real workloads from HPC systems, we aim to see what the impact of adding such new hardware has on the efficiency of the system with respect to latency and throughput for single and workflow jobs.

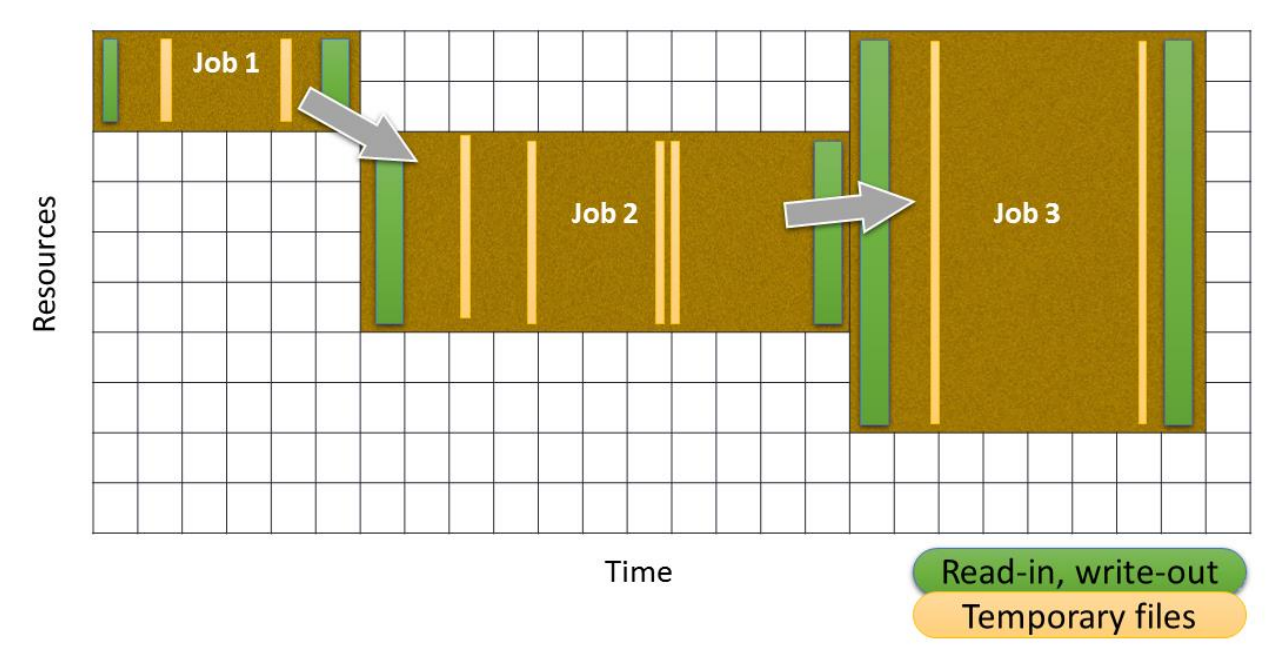
A map of scheduled jobs showing data dependencies
between them – looking for methods of scheduling these
efficiently is one task of this project.
Project Mentor: Dr. Nick Johnson
Project Co-mentor: Manos Farsarakis
Site Co-ordinator: Ben Morse
Learning Outcomes:
The student will learn about different HPC scheduling algorithms, how they interact with the components of a modern HPC system and how upcoming hardware might change the implications of some scheduling assumptions. The student will also learn and develop skills in C++ programming, GNU/Linux and general software engineering.
Student Prerequisites (compulsory):
Some knowledge of C++ including compiling and debugging (using a debugger); general software engineering including version control using git; familiarity with HPC terminology and modern HPC technology.
Student Prerequisites (desirable):
Knowledge of job scheduling algorithms.
Training Materials:
Nothing specific, but general materials on git/C++ from the web should be read to be up to date prior to arrival.
Workplan:
The first two weeks will be spent in the training session and then getting set up with tools (laptop etc.) and learning the code from the mentors. By learning the code, a plan for work will be devised based on what the student wants to do (implementation or algorithm development, software engineering) in the subsequent weeks and the required order (some tasks may require engineering before work can begin). The remaining weeks will be spent on the work, working alongside the mentors before writing up in week 8 and giving a group talk on the project.
Final Product Description:
- A study of the impacts of new types of hardware on the efficiency of scheduling systems for HPC;
- Improved simulator code (better featured, fewer bugs, more performance);
- Additional algorithms (or tweaked algorithms) implemented.
Adapting the Project: Increasing the Difficulty:
The number, complexity and features of the algorithms could be increased to make the project more difficult.
Adapting the Project: Decreasing the Difficulty
To decrease the difficulty, the student could work on a more straight-forward implementation of scheduling algorithms; improving the speed of the simulator.
Resources:
The student will require access to a laptop, the existing simulator code and input data. All of which will be provided by the host.
Organisation:
Edinburgh Parallel Computing Centre (University of Edinburgh)


Leave a Reply