Discovering the secrets of El Niño

El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a major climate pattern that consists of oscillations of the meteorological parameters in the equatorial Pacific ocean. It happens every 2 to 7 years but it is not periodically stable.
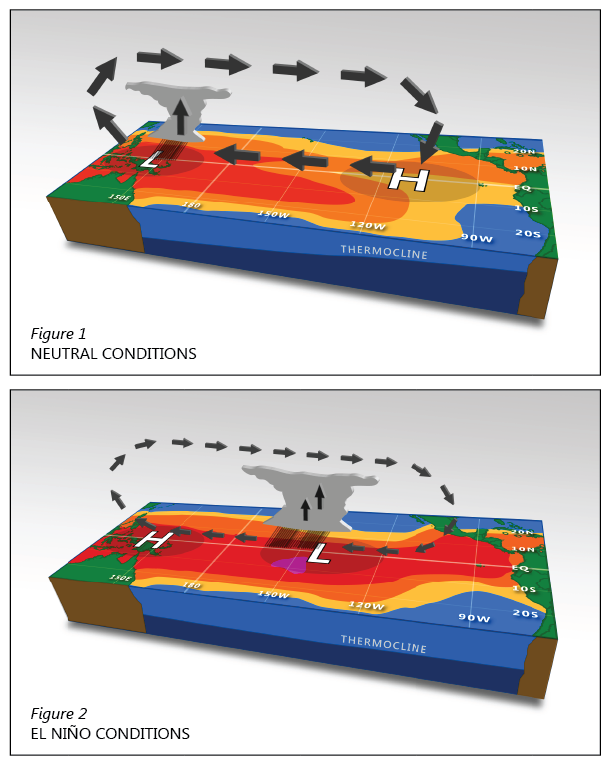
Normal climatic conditions and El Niño conditions in the Pacific Ocean
What is ENSO?
Normal weather conditions are the following:
- Low pressures (L) in the Pacific islands, causing rainy weather and warm ocean waters.
- High pressures (H) near the eastern American coast, causing colder ocean waters and less rain.
When ENSO happens, this situation is drastically changed:
- The low and high pressures switch places (this is why it is called Southern Oscillation), causing the rain to move towards the west.
- Because of this, warm ocean waters move towards the west, causing alterations in the fishing patterns in South America.
ENSO is a phenomenon that involves the ocean, the atmosphere and the land in such a huge scale that it affects weather in the entire world, changing precipitations, temperature and wind flows along Earth. Among all of these consequences, we can highlight the following ones: massive forest fire in Indonesia, since it stops raining in that zone, flooding in Peru caused by a severe amount of rain in a small period of time, drought in India because of abnormally light monsoon months and an overall warming of the global climate temporarily.
All of these makes ENSO an important part of the weather climate cycle, a phenomenon which is worth studying and that is why I am working at the ICHEC in Dublin this summer.
What am I doing in Dublin?
First of all, I will analyze how past El Niño events have been, whether it is possible to find some trend in these events and I will also check how future El Niño events are predicted to be. Secondly, I will study how El Niño impacts other parts of the world, what is the correlation between all these events and how much was the impact in the last event. Finally, I will take a look at all the available forecast systems one season ahead, to check their accuracy and precision in detecting future El Niño events.

Abnormal ocean surface temperatures [ºC] observed in December 1997 during the last strong El Niño. Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:El-nino.png
El Niño is a phenomenon that takes places, normally, all year round but the moment in which water warms the most in the Peru coast is in December. This is why fisherman associated this phenomenon with the Christmas holidays and called it “El Niño” that literally means “The boy” after the nativity in the end of December.
