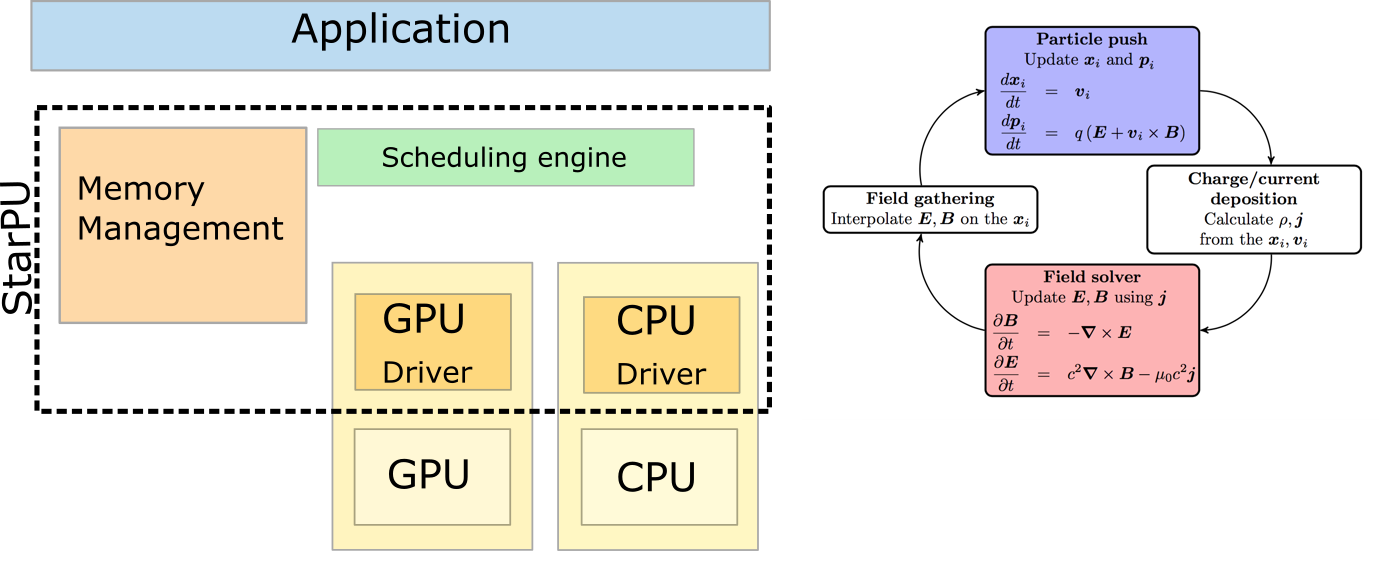
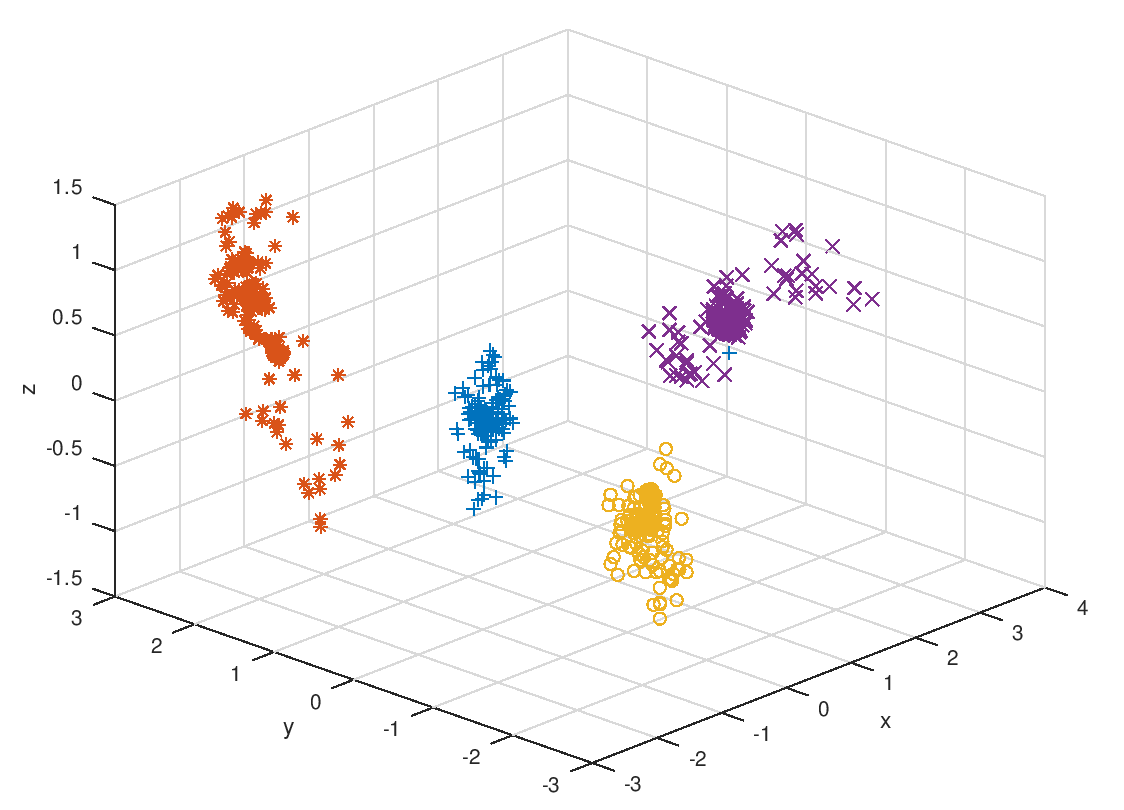
Project reference: 2024 Creating a mesh* – a discretized surface enclosing a given spatial object – is a compute-intensive task central to many scientific fields ranging from physics (Maxwell’s Eq., CFD, MD) to computational biology (PB, MM/PBSA, cryo-EM, Struct. Bio). …